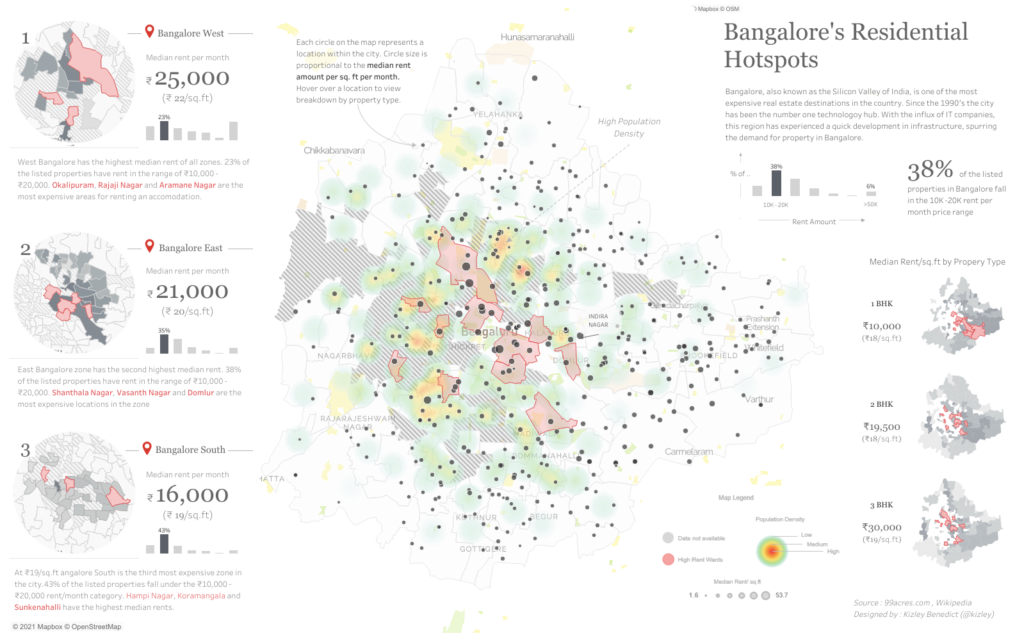
What is business intelligence: Learn how data is shaping the business world

Each day, the world produces over 2.5 quintillion data, according to a study by Domo group. Given that this study was conducted in 2018, this number is likely to have grown by leaps and bounds by now. All this data serves as a treasure trove for companies who use it to gain valuable insights about their users. This has led to the emergence of many data-related technologies and business intelligence is one of them.
Business intelligence definition
Business intelligence (BI) is the process of collecting, analysing, and visualising data to gain insights that drive the business forward.
A simple example of a company using this is Starbucks. The company uses customer data such as purchase history to send them the most relevant offers and deals, thus increasing their conversion rate.
Now that we know what business intelligence is, let’s learn about the process of business intelligence.
How does business intelligence work?
Business intelligence lies at the intersection of data collection, data analysis, reporting, and decision-making.
1. Collecting data
Data can be collected from multiple sources such as websites, social media, sales and marketing campaigns, finance department, etc. Since the data comes from varied sources, it is in different formats such as Excel, JSON, CSV, etc. Moreover, they contain duplicates. So, the data is not fit for analysis yet and needs to be transformed.
2. Preparing and transforming data
Once the data is collected from various sources, it is brought together in one place and organized. This is done through ETL.
ETL stands for extract, transform, and load.
It is the process of extracting data from multiple sources, removing errors from it, converting to a desired format, and uploading it to a data warehouse.
Data warehouse, as the name suggests, is a central place to store data. The data is usually historical meaning that it is not being generated in real-time. The data is then used for analytics and business reporting.
3. Analysing data
Once the data is integrated, it is analysed. The goal of this analysis is to understand how the company was doing in the past as well as how it’s performing now and why.
This includes answering questions related to business performance such as – Did we meet the sales target?
The data can also be used for financial analysis, spotting trends, and so on. The analyst also probes the data to understand the ‘why’ behind the trend.
For example, the number of sales was higher in the months of May and June compared to July. An analyst should be able to figure out why and help you fine tune your business strategy.
4. Visualising data
After the analysis, the findings can be turned into digestible visuals such as charts and graphs. This is done through BI tools such as Tableau and Power BI.
5. Communicating with stakeholders
Now that you have investigated the data and come up with insights, it is show time!
The insights are communicated in an easy-to-understand format to the stakeholders. This is generally done through reports or dashboards.
These dashboards can give you insights such as website traffic, revenue generated, conversion rate, etc.
6. Making strategic decisions
Based on the reports, the business leaders understand how the business has performed and set targets.
7. Monitoring performance
Once the decisions have been communicated to the management, the team starts working on the goals and monitors their performance through self-service BI.
What is the importance of business intelligence?
Here are the most common benefits of business intelligence:
1. Increases revenue
BI helps you learn more about consumer behavior such as buying patterns. You can use this to improve business models such as product recommendations, marketing campaigns, supply and demand, etc. Basically, it can help you identify what the customer wants and lead to greater customer satisfaction that in turn leads to higher revenue.
2. Helps you track performance
BI helps different teams in measuring their performance through key performance indicators such as the number of visitors, engagement, and sales.
Such visibility on performance can help teams decide if they should continue with the current business strategy or make changes.
For example, if you have added or modified a product feature and there is a dip in the engagement, you can reconsider the changes or dig deeper into what caused disengagement.
3. Helps avoid setbacks
Through data, you can recognise the pain points of your users. Additionally, you can also identify risks in your business. Both of these can help businesses in avoiding major setbacks.
4. Leads to better human resource management
BI in human resources can help you create a more engaged and efficient workforce. For example, Google uses data to understand what causes attrition. This helps them in addressing the issues early on and improves retention rate.
Top BI tools
The BI infrastructure contains tools and technologies used for collecting data, analysing data, and reporting. Some of the most popular tools include:
1. Tableau
Tableau came into being as an academic project by 3 Stanford students who wanted to make data easier to understand through visualisation. To do this, it uses a simple interface which converts drag and drop actions into data queries. This leads to the creation of reports or dashboards.
Tableau contains various features that help in different stages of the business intelligence process. It assists in data cleaning and preparation through its tool Tableau Prep Builder. Next, it allows you to connect to data, explore, and visualise it through Tableau Desktop or Tableau Public. Lastly, it creates a safe passage to share the data or collaborate on reports through Tableau Server and Tableau Online.
Another thing that makes Tableau such a robust platform is the frequent updates and fixes.
 Source: Tableau Public
Source: Tableau Public
2. Power BI
This BI tool by Microsoft is user-friendly and one of the most affordable options in the market. Like Tableau, it can be used to prepare, analyse, visualise, and share data. In addition to sharing data with your team, you can also embed it into your website.
Power BI lets you tackle data of all shapes and sizes right from an Excel sheet to a huge database. For companies that already use Microsoft products such as Office 365, the data can be easily connected to Power BI.
It also offers pre-built dashboards for some commonly-used technologies such as Google Analytics and Salesforce.
Power BI is used by Nestle, Adobe, and HP.
3. Google Data Studio
This is a completely free data visualisation tool. You can think of it as an advanced version of Google Analytics (GA).
While GA works with limited data sources, Google Data Studio lets you connect to various data sources such as Google Ads, Google Sheets, YouTube, and databases. Since this tool is a Google product, it can be especially helpful if your team uses G Suite extensively.
Unlike Tableau and Power BI, this is only available in the web version. Another limitation is that the visualisations are not sophisticated as other BI tools.
4. Sisense
This tool is used for end-to-end business intelligence processes from data collection to sharing dashboards. It is one of the best BI tools for creating interactive dashboards which can be viewed on any device.
Sisense clients include Philips, Policybazaar, and GitLab.
The above-mentioned BI tools are just the tip of the iceberg and there are several other tools such as Zoho Analytics, QlikView, and Domo that come with their USPs.
Careers in business intelligence
If you curious to know what kind of roles does the field offer, then here are some entry-level BI careers:
1. Business intelligence engineer
This is a back-end role. BI engineers are responsible for the ETL process i.e. extracting, transforming, and loading data.
2. Business intelligence developer
Once the data is prepared by BI engineers, the BI developers prepare dashboards for end-users.
3. Data analyst
They delve into data, uncover trends, predict outcomes, and create data visualisations. This is one of the most in-demand tech careers in India.
4. Business analyst
They are responsible for analysing business problems and defining business requirements. Although they may look at the current data to understand the problem, they don’t work with data as extensively as the data analyst.
While each business intelligence professional needs special skills, here are a few common skills that each of them needs to make it in the industry:
Soft skills
1. Problem-solving
Using data to solve business problems is at the heart of business intelligence. Consequently, problem-solving in a structured way is a key skill to pursue a career in the field.
2. Business acumen
As a BI professional, you will be responsible for understanding business’ pain points and uncovering insights that can help solve them. Hence, you need to have an understanding of how the business functions.
3. Communication
Business intelligence is a cross-functional role and requires you to communicate with various stakeholders, be it customers or internal teams. So, good communication skills are a must.
Hard skills
1. Understanding of databases
Most companies use databases as the repository for their data. So you should have an understanding of how they work as this will be a part of your day-to-day work.
2. Proficient in a query language
As you will be working with databases, you need to know how to query data. The most commonly-used language is SQL.
3. Know-how of a BI tool
To kickstart your BI career, you should at least know one business intelligence tool as this can help you in adapting to other tools.
This was a glimpse into the world of business intelligence. If you want to try your hand at data visualisation, check out Internshala’s Tableau online course or Power BI course. You can use BLOG10 to get a discount of 10%.
Image credits: <a href=’https://www.freepik.com/free-photos-vectors/people’>People vector created by jcomp – www.freepik.com</a>



